Netty Netty是一个由JBoss提供的java开源框架,
Netty是一个异步的, 基于事件驱动的网络应用框架, 用于快速开发高性能, 高可用的网络IO程序.
Netty主要针对在TCP协议下, 面向client端的高并发应用, 或者Peer-to-Peer场景下的大量数据持续传输应用.
Netty 主要基于NIO
netty 是基于 NIO 那先简单介绍一下IO
IO模型
I/O模型: 简单理解就是用什么方式进行数据的发送和接收, 决定了通信的性能
三种IO模型:
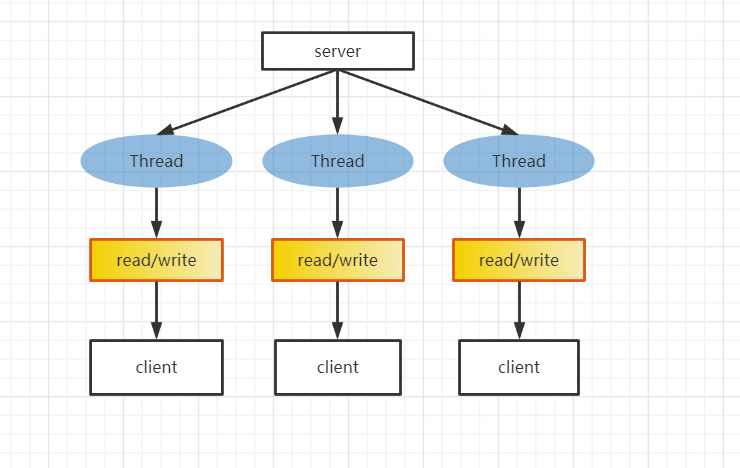
BIO(同步并阻塞) 一个连接创建一个线程, 客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程处理, 如果连接不进行操作还会造成不必要的开销
BIO
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.net.ServerSocket;import java.net.Socket;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class MainDemo { void serverBIo () throws IOException { Socket accept = null ; ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket (9999 ); System.out.println("lianjie..." ); while (true ) { accept = socket.accept(); Socket finalAccept = accept; executorService.submit(() -> { handler(finalAccept); }); } } private void returnMsg (Socket finalAccept, String s) throws IOException { System.out.println("return" ); OutputStream outputStream = finalAccept.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write(s.getBytes()); outputStream.flush(); } private void handler (Socket accept) { byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 ]; InputStream stream = null ; String s = "" ; try { stream = accept.getInputStream(); System.out.println("in" ); while (true ) { int i = stream.read(bytes); s = new String (bytes) + ":::" + Thread.currentThread().getName(); if (i != -1 ) System.out.println(s); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { stream.close(); returnMsg(accept, s); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main (String[] args) { MainDemo server = new MainDemo (); try { server.serverBIo(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
缺点:
需要独立的线程 并发大时 ==需要大量的线程进行处理== 并且 如果没有读写操作 线程会阻塞在Read上 造成资源浪费
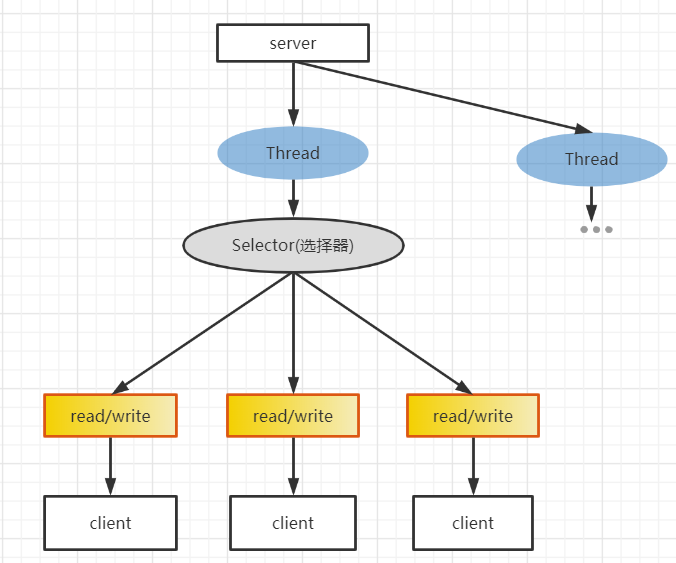
NIO(同步非阻塞) 和BIO相比 实现了一个多路复用 的功能 服务器可以用一个线程处理多个连接, 多路复用器进行轮询如果有IO请求就处理
NIO
三大核心: Selector Channel Buffer
具体方式:
image-20200825235215229
NIO的通讯:
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;import java.nio.channels.Selector;import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.Set;public class GroupChatClient { private final String HOST = "127.0.0.1" ; private int PORT = 6667 ; private Selector selector; private SocketChannel socketChannel; private String userName; public GroupChatClient () throws IOException { selector = Selector.open(); socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress ("127.0.0.1" , PORT)); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false ); socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); userName = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1 ); System.out.println(userName + " is ok ~" ); } public void sendInfo (String info) throws Exception { if (info.equalsIgnoreCase("exit" )) { socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes())); socketChannel.close(); socketChannel = null ; return ; } info = userName + " 说: " + info; try { socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes())); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void readInfo () { try { int readyChannels = selector.select(); if (readyChannels > 0 ) { Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator(); while (keyIterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = (SelectionKey) keyIterator.next(); if (sk.isReadable()) { SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) sk.channel(); ByteBuffer buff = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); sc.read(buff); String msg = new String (buff.array()); System.out.println(msg.trim()); } keyIterator.remove(); } } else { System.out.println("没有可用channel ..." ); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { GroupChatClient chatClient = new GroupChatClient (); new Thread () { public void run () { while (true ) { chatClient.readInfo(); try { Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }.start(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); while (scanner.hasNextLine()) { String msg = scanner.nextLine(); chatClient.sendInfo(msg.trim()); } } }
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.*;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Iterator;public class GroupChatServer { private Selector selector; private ServerSocketChannel listenerChannel; private static final int PORT = 6667 ; public GroupChatServer () { try { selector = Selector.open(); listenerChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); listenerChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress (PORT)); listenerChannel.configureBlocking(false ); listenerChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); printInfo("服务器 ok......." ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void listen () { try { while (true ) { int count = selector.select(); if (count > 0 ) { Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); if (key.isAcceptable()) { SocketChannel sc = listenerChannel.accept(); sc.configureBlocking(false ); sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); System.out.println(sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress().toString().substring(1 ) + " 上线 ..." ); key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); } if (key.isReadable()) { readData(key); } iterator.remove(); } } else { System.out.println("waitting ..." ); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void readData (SelectionKey key) { SocketChannel channel = null ; try { channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); int count = channel.read(buffer); if (count > 0 ) { String msg = new String (buffer.array()); printInfo(msg); key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ); sendInfoToOtherClients(channel, msg); } buffer.clear(); } catch (IOException e) { try { printInfo(channel.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress().toString().substring(1 ) + " 离线了 ..." ); key.cancel(); channel.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } } public void sendInfoToOtherClients (SocketChannel except, String msg) throws IOException { System.out.println("服务器进行消息转发 ..." ); for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) { Channel targetchannel = key.channel(); if (targetchannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetchannel != except) { SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetchannel; ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()); dest.write(buffer); } } } private void printInfo (String str) { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ); System.out.println("服务器接收到消息 时间: [" + sdf.format(new java .util.Date()) + "] -> " + str); } public static void main (String[] args) { GroupChatServer server = new GroupChatServer (); server.listen(); } }
AIO(异步非阻塞)一般用于长稳定的连接 Reactor模式 什么是Reactor wiki上reactor的解释
The reactor design pattern is an event handling pattern for handling service requests delivered concurrently to a service handler by one or more inputs. The service handler then demultiplexes the incoming requests and dispatches them synchronously to the associated request handlers.
说人话就是来处理一个或者多个输入请求的事件处理模式(基于事件驱动). 采用IO复用监听事件
服务器端将传入的请求分派到相应的线程进行处理所以也是Dispatcher模式
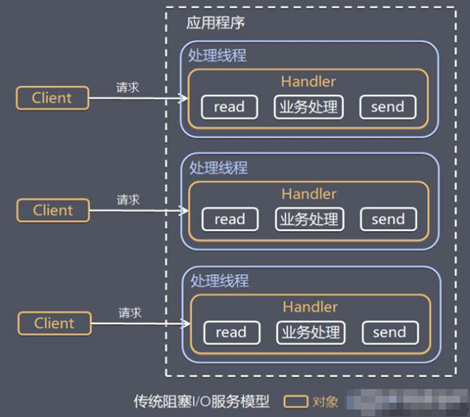
先看一下传统的模型:
image.png
问题分析
当并发数很大,就会创建大量的线程,占用很大系统资源
连接创建后,如果当前线程暂时没有数据可读,该线程会阻塞在read 操作,造成线程资源浪费
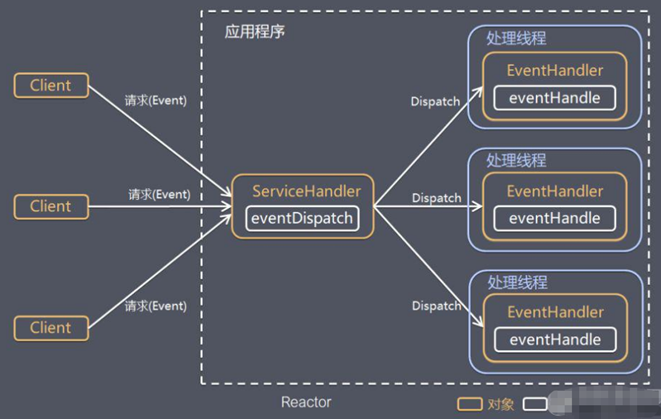
Reactor模型(IO复用)
image.png
Reactor 模式,通过一个或多个输入同时传递给服务处理器 的模式(基于事件驱动)
服务器端程序处理传入的多个请求,并将它们同步分派到相应的处理线程, 因此Reactor模式也叫 Dispatcher模式
Reactor 模式使用IO复用监听事件, 收到事件后,分发给某个线程(进程), 这点就是网络服务器高并发处理关键
三种reactor实现
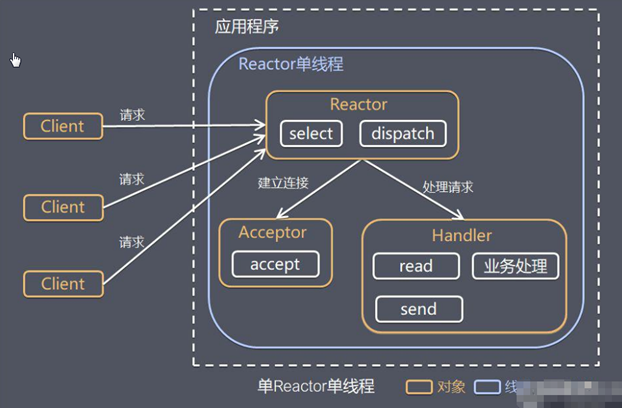
单reactor单线程实现方式
单线程
select:通过一个阻塞对象监听多路连接请求
实现流程:
客户端的请求由Reactor中的select监听请求类型 :
建立连接(Accept来创建handler对象处理业务)2. 其他请求由handler来处理
因为是的单线程所以请求多或者业务处理耗时很大时还是会发生阻塞 情况
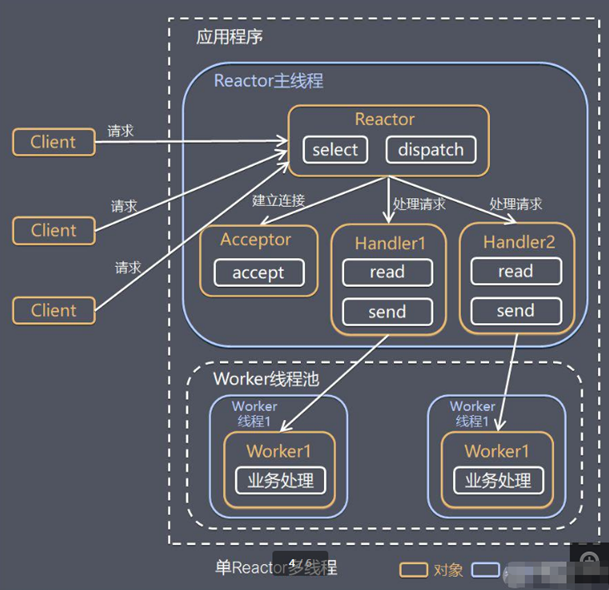
单reactor多线程
多线程
还是由reactor监听分发 但是handler不做业务处理只作事件的响应 分发给对应的worker线程池中的worker来处理(可以继续响应消息), worker返回结果由handler发送回客户端
由于业务在线程池中处理 性能高于单线程 但是多线程的数据处理很麻烦 而且reactor是在单线程情况下 还是会有性能瓶颈的
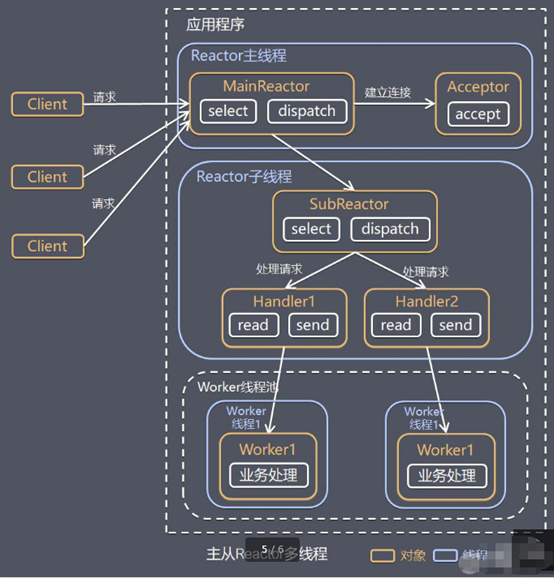
主从reactor
主从reactor
我们可以让 Reactor 在多线程中运行
reactor的主线程监听到消息由MainReactor分发 并且只是处理连接(Accept)请求
其他的请求分发到子Reactor(SubReactor), SubReactor处理客户端(除连接)的请求,并且等待worker线程处理结果发回客户端
主线可以对应多个子线程 每个子线程可以对应多个worker线程
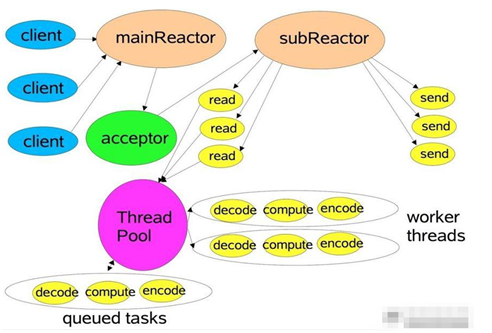
Scalable IO in Java 对 Multiple Reactors 的原理图解:
image.png
主从reactor的优点
父线程与子线程的数据交互简单职责明确,父线程只需要接收新连接,子线程完成后续的业务处理。
父线程与子线程的数据交互简单,Reactor 主线程只需要把新连接传给子线程,子线程无需返回数据。
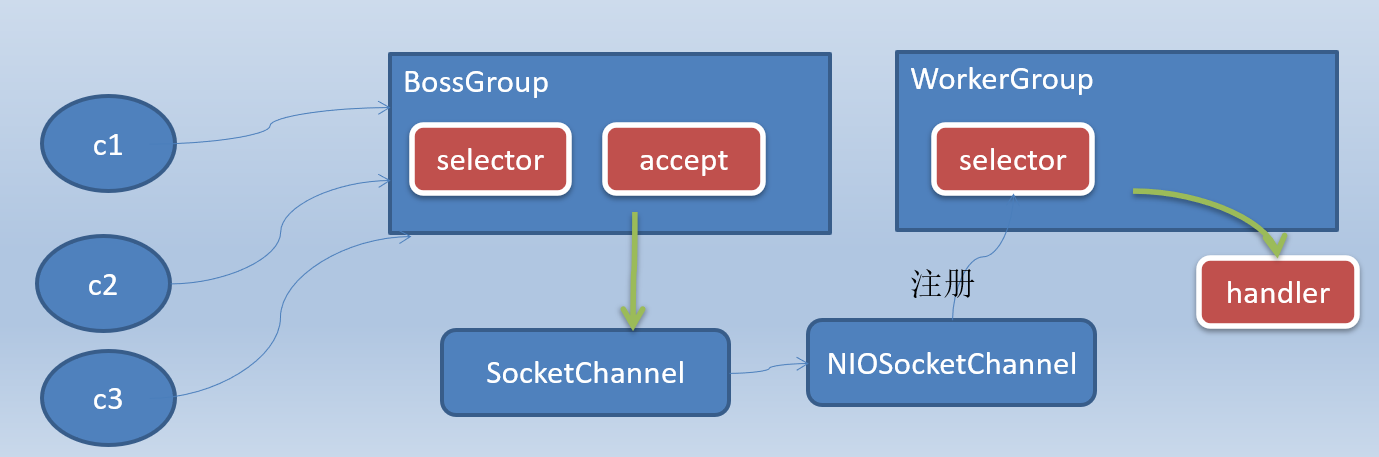
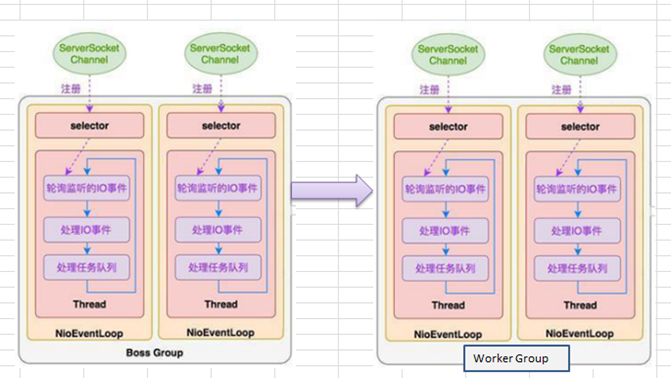
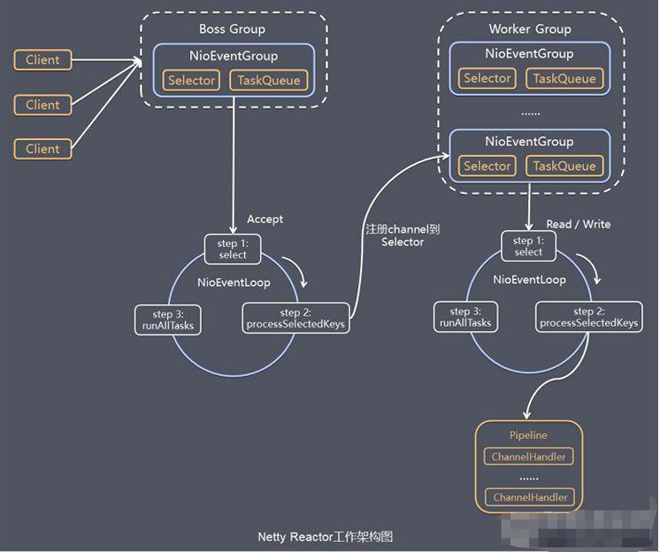
Netty模型 上面说了主从reactor Netty是一个主从多线程模型的支持
netty模型简单介绍 和reactor的主从模型很像 在此基础上实现了多个”Reactor”
netty
netty模型
netty详细模型
image.png
客户端-服务端实现(Netty的TCP实现) java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 public class NettyServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup (); NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup (); ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap (); bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { System.out.println("init..." ); socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler ()); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(6668 ).sync(); System.out.println("server is ready..." ); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Server:" + ctx); ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("客户端发来的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } @Override public void channelReadComplete (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("服务端发送" ); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端发:hello client(>^ω^<)喵123123" , CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public class NettyClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup (); Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap (); bootstrap.group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { System.out.println("init kehu" ); socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler ()); } }); System.out.println("client is ready" ); ChannelFuture sync = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 6668 ).sync(); sync.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } } public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { super .channelActive(ctx); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello clientHandler" , CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { super .channelRead(ctx, msg); ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("服务端接收到的是:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } }
任务队列 - TaskQueue 当很耗时的任务在PipeLine中可以将这个任务异步到处理队列(TaskQueue)
使用场景:
用户程序自定义普通任务
java
1 ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable ().run);
用户自定义定时任务 - ScheduleTaskQueue
java
1 ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(() -> {}, 5 , TimeUnit.HOURS);
非当前Reaactor线程调用Channel的方法
推送系统:根据客户的标识,找到Channel引用,调用Write类方法向用户推送消息,就会进入到这种场景里面,Write会提交到任务队列中被异步消费。
对上述方案说明
Netty抽象出两组线程池 , BossGroup站门负责接收客户端的连接,WorkGroup负责网络的读写。
NioEventLoop表示一个不断循环执行处理任务的线程,每个NioEventLoop有一个select,用于监听绑定在socket上的网联络通道。
NioEventLoop采用串行设计。(读取->解码->编码->发送)。
NioEventLoopGroup下有多个NioEventLoop
每个NioEventLoop中包含一个Select,一个NioChannel
每个NioChannel只会绑定在唯一的NioEventLoop上,并且都有自己的一个ChannelPipeline
异步操作
Listen_result(不需要等待),Bind,Write,Connect都是异步监听操作。返回一个ChannelFuture用来监听
调用时不会立即有结果,通过Future-Listener机制,用户可以主动获取。
Netty的异步模型在future(Future-Listener机制体现)和callback(回调)之上。
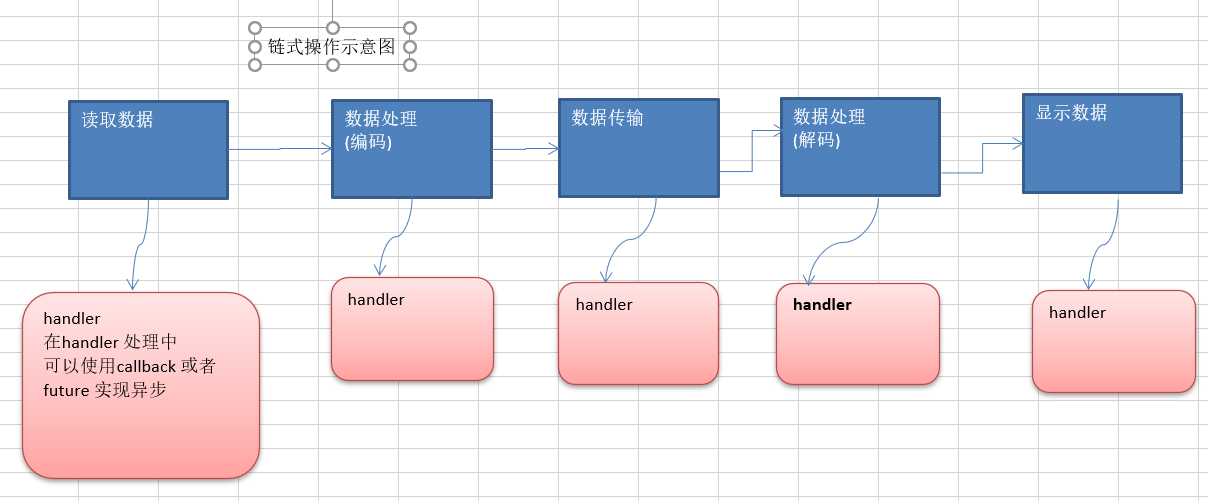
==链式模型==
image.png
==Future-Listener机制==
当Future对象创建时,处于非完成状态,返回一个ChannelFuture获取操作的状态,注册监听函数来执行完成后的操作。
isDone / isSuccess / getCause / ……操作
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 serverBootstrap.bind(port).addListener(future -> { if (future.isSuccess()) { System.out.println(newDate() + ": 端口[" + port + "]绑定成功!" ); } else { System.err.println("端口[" + port + "]绑定失败!" ); } });
Http 服务 java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class TestServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ EventLoopGroup bossGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup (); EventLoopGroup workerGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap=new ServerBootstrap (); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class). childHandler(new TestServerInitializer ()); ChannelFuture channelFuture=serverBootstrap.bind(6668 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class TestServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline=ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast("httpServerCodec" ,new HttpServerCodec ()); pipeline.addLast("testHttpServerHandler" ,new TestHttpServerHandler ()); } }
java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 public class TestHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <HttpObject> { int count = 4 ; @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception { if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) { System.out.println(msg.getClass()); System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); HttpRequest httpRequest= (HttpRequest) msg; URI uri=new URI (httpRequest.uri()); System.out.println("请求方法名:" +httpRequest.method().name()); ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello! 我是服务器" + (++count), CharsetUtil.UTF_8); FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse (HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, content); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain" ); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, content.readableBytes()); ctx.writeAndFlush(response); } } @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelActive" ); super .channelActive(ctx); } @Override public void channelRegistered (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelRegistered" ); super .channelRegistered(ctx); } @Override public void handlerAdded (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("handlerAdded" ); super .handlerAdded(ctx); } @Override public void channelInactive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelInactive" ); super .channelInactive(ctx); } @Override public void channelUnregistered (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelUnregistered" ); super .channelUnregistered(ctx); } }
由于HTTP协议的无状态
所以刷新会重置handler和对应的Pipeline
image.png
不知道为什么谷歌浏览器访问不到 todo
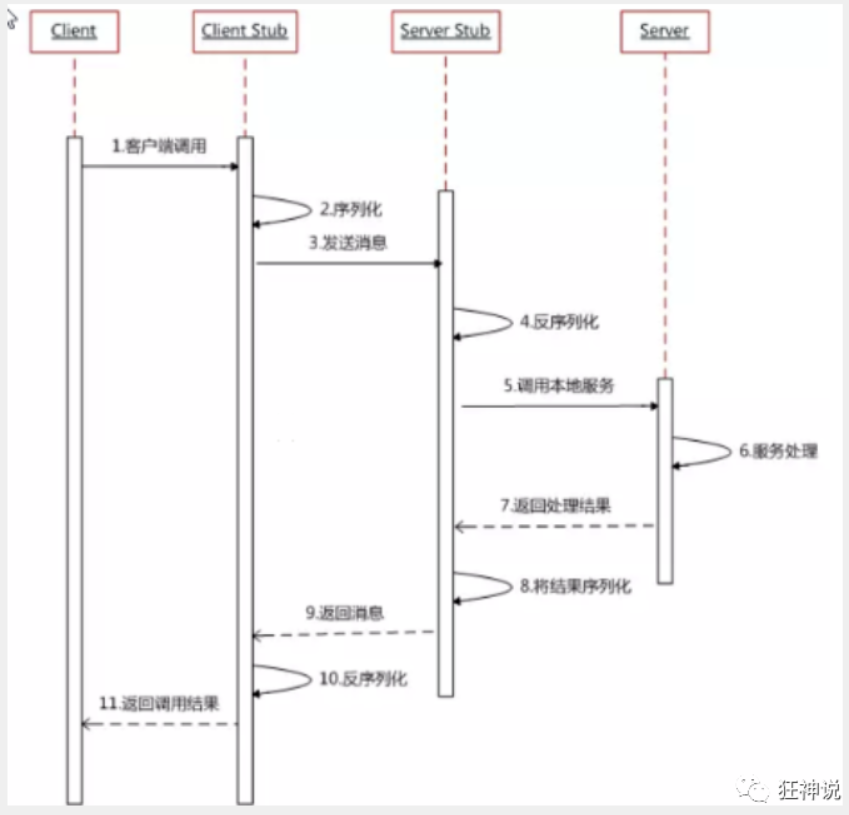
什么是RPC RCP(Remote Procedure Call) 远程调用过程
远程调用过程? ()这玩应就跟把Socket翻译成套接字一样 说个锤子)
那有远程调用就有本地调用 – 本地就是在自己的服务里进行交互; 那很显然远调就是 自己的服务与别的服务进行交互
通信过程
image.png
举个栗子🌰
普通架构计, 做一个加法计算 主函数调用 计算的add方法
分布式呢就是把计算的服务单独拿出来了 但是怎么获取到计算服务的方法呢?
可以在计算服务加一个接口? 但是不能每一次都发起http请求呀
如何让使用者感受不到远程调用呢?
java
1 2 @Reference private 计算 name;
使用代理模式 和Spring的IOC 一起, 注入需要的对象
核心模块 通讯 和 序列化解决分布式系统中,服务之间的调用问题。 远程调用时,要能够像本地调用一样方便,让调用者感知不到远程调用的逻辑。
dubbo
dubbo流程
参考资料 如何给老婆解释什么是RPC
NIO通信模型案例
Scalable IO in Java (一本书)